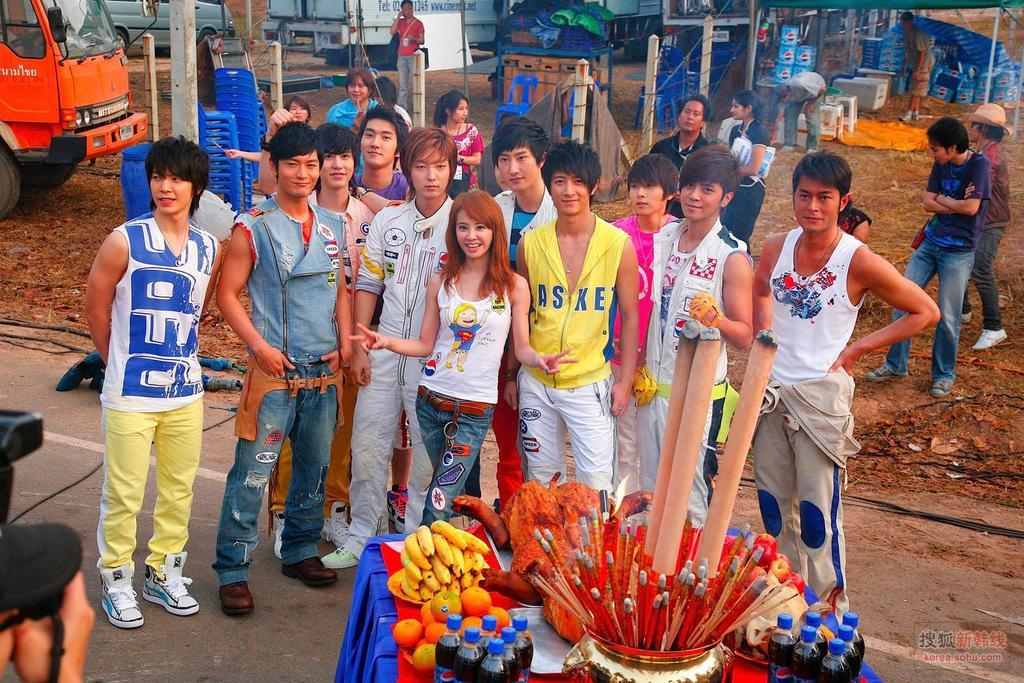|
 ความคิดเห็นที่ 126
ความคิดเห็นที่ 126 |

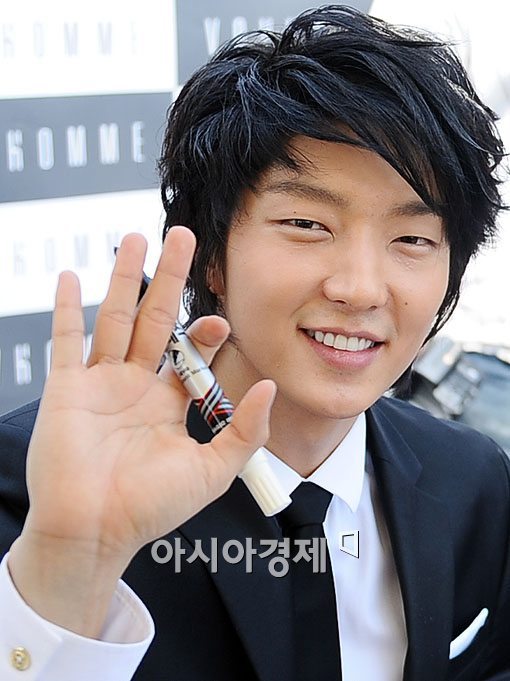
มาเติมวิชาการร้อนๆอีกหน่อย ฮี่ๆๆๆๆ
คุณดิวจร๋าาาาา แบบนี้อ๊ะป่าวค้า สามเหลี่ยมที่คุณดิวพูดถึงมะกี้
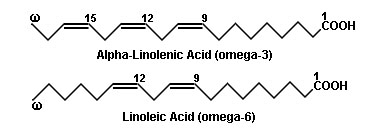
ปอ ลอ...แม่บ้านเค้อออ รูปนี้เป็นกรดไขมันของจุนห่ะ(-____________-)'''
(มันเอาจุนมาเกี่ยวอีกจนได้ห่ะ)
อธิบายนิดนุง (แปะในบ้านนี่แหละ ฮว่าๆๆๆๆ)
18:2 ก็หมายความว่า ตัวเลขตัวหน้าคือจำนวนคาร์บอนอะตอมที่เกาะกันเป็นสาย chain ค่ะ ส่วนตัวเลขอันหลังคือจำนวน double bond ที่อยู่บน structure ของfatty acid ตัวนั้นๆค่ะ ส่วนกรดไขมันที่เป็นโอเมก้า(มีโอเมก้าเกาะอยู่ มักใช้อักษรภาษากรีกค่ะ) ร่างกายเราไม่สามารถสร้างเองได้ จึงต้องกินเข้าไปอย่างเดียวค่ะ
ลองอ่านนี่ดูนะคะ เผื่อจะช่วยได้(^________^)'''' อันนี้เค้าเขียนแบบ Big picture ไม่ลงลึกมากนัก แต่ก็ช่วยอธิบายตรงที่สงสัยว่าคืออะไรได้จ๊ะ(อ่านแล้วดูรูปไปด้วยนะคะ)
Hope this help>>>>(*___________________*)
What are Omega-3 and Omega-6 fatty acids?
Omega-3 (ω3) and omega-6 (ω6) fatty acids are unsaturated "Essential Fatty Acids" (EFAs) that need to be included in the diet because the human metabolism cannot create them from other fatty acids. Since these fatty acids are polyunsaturated, the terms n-3 PUFAs and n-6 PUFAs are applied to omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, respectively. These fatty acids use the Greek alphabet (α,β,γ,...,ω) to identify the location of the double bonds. The "alpha" carbon is the carbon closest to the carboxyl group (carbon number 2), and the "omega" is the last carbon of the chain because omega is the last letter of the Greek alphabet. Linoleic acid is an omega-6 fatty acid because it has a double bond six carbons away from the "omega" carbon. Linoleic acid plays an important role in lowering cholesterol levels. Alpha-linolenic acid is an omega-3 fatty acid because it has a double bond three carbons away from the "omega" carbon. By subtracting the highest double-bond locant in the scientific name from the number of carbons in the fatty acid we can obtain its classification. For arachidonic acid, we subtract 14 from 20 to obtain 6; therefore, it is an omega-6 fatty acid. This type of terminology is sometimes applied to oleic acid which is an omega-9 fatty acid.
In these simplified structural formulas of unsaturated fatty acids, each angle represents a carbon atom. Notice that all the double bonds have the Cis configuration.
DHA (docosahexaenoic acid) and AA (arachidonic acid) are both crucial to the optimal development of the brain and eyes. The importance of DHA and AA in infant nutrition is well established, and both substances are routinely added to infant formulas. Excessive amounts of omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids and a very high omega-6/omega-3 ratio have been linked with pathogenesis of many diseases, including cardiovascular disease, cancer, and inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. The ratio of omega-6 to omega-3 in modern diets is approximately 15:1, whereas ratios of 2:1 to 4:1 have been associated with reduced mortality from cardiovascular disease, suppressed inflammation in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, and decreased risk of breast cancer. Some researchers have suggested that there is not very strong evidence for the benefits of these ratios, and that it may be better to increase the consumption of omega-3 fatty acids rather than decrease the consumption of omega-6 fatty acids because a reduction of polyunsaturated fats in the diet would increase the incidence of cardivascular disease.
แก้ไขเมื่อ 11 ม.ค. 53 21:47:58
| จากคุณ |
:
หมูมืด  
|
| เขียนเมื่อ |
:
11 ม.ค. 53 21:45:40
|
|
|
|
 |