|
 ความคิดเห็นที่ 156
ความคิดเห็นที่ 156 |

ความสมมาตรในความหมายของซอนนิมในทาง anatomy ก็คือ ยังไงร่างกายเราก็สมมาตรค่ะ ยกเว้น organ บางอย่างที่อยู่ข้างใน
อันนี้เป็นความรู้ทาง anatomy เกี่ยวกับ Body symmetry เพื่อให้เข้ากะบรรยากาศ(วิชาการหนักไปป่าวฟระ ฮว่าๆๆๆ)
เอาเป็นว่าแปะให้แม่บ้านที่ชอบ Technical term ก็แล้วกันจ๊ะ อิ อิ
(นะจ๊ะคุณดิว)
============================================
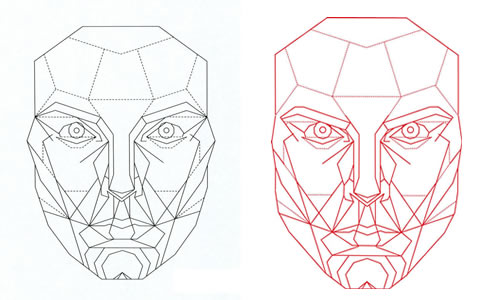
Body symmetry is the description of the arrangement of a body and its parts and systems in a balance. The term symmetry implies that the body can be split in at least one way into equal, virtually identical halves. There are essentially four types of body symmetry known in the Animal Kingdom: asymmetry, bilateral symmetry, radial symmetry, and spherical symmetry.
ASYMMETRY
Asymmetry, as the name implies, is a body that lacks any visible symmetry. (The prefix "a-" means "without.") Creatures with this type of symmetry are typically amorphous, with no discernible "left" or "right" side. There is no definite plane through which one can separate the body into equal parts.
The sponge (Phylum Porifera) is really the only animal that exhibits asymmetry. Unlike its famous cartoon counterpart (which exhibits another symmetry), a sponge resembles a loose, porous arrangement of tissue that seems to grow in random patterns. In most species, sponges eat, breathe, and excrete waste through the same pores and are fixed at the bottom. However, one cannot split a sponge into two mirror-images in any direction.
Another organism that exhibits asymmetry is everyone's favorite microorganism, the amoeba.
BILATERAL SYMMETRY
"Bi-" is a prefix meaning "two," so a bilaterally symmetrical animal is one whose body is capable of being split in two identical halves. Creatures with this type of body arrangement have clearly identifiable left and right, top and bottom, front and back sides. These also tend to have a progressive feature called "cephalization" where sensory organs are located near the "head" ("cepha-" means "head"), which aids in detecting danger all from one location. Bilateral symmetry brings with it a whole host of directional references, including anterior and posterior (head and bottom), and ventral and dorsal (front and back).
Most animals are bilaterally symmetrical. Humans exemplify this most obvious symmetry. If the human body was split right down the middle, from the top of the head, down between the eyes and downward, the end result would be two mirror-images. The typical human body has left and right eyes, hands, kidneys, and knees. The same goes for horses, alligators, eagles, frogs, and sharks (as well as the aforementioned cartoon sponge).
However, with bilateral symmetry, the body shapes are not capable of being separated laterally, say across the stomach. The top and bottom halves are not even close to being similar; hence, the "bi-" or "two" specification.
credit: Body symmetry explained; Medical Science by Levi's Johnson
จุน: กราบซอนนิมครับ พอเถอะครับ สาระเยอะเกิน แม่บ้านไม่ปลื้ม......
ซอนนิม: (*__________*)
| จากคุณ |
:
หมูมืด  
|
| เขียนเมื่อ |
:
17 ม.ค. 53 16:38:37
|
|
|
|
 |