|
Hebrew (/ˈhiːbruː/) (עִבְרִית ʿIvrit, [ʔivˈʁit] (help·info) or [ʕivˈɾit] (help·info)) is a West Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Culturally, it is considered by Jews and other religious groups as the language of the Jewish people, although other Jewish languages had originated among diaspora Jews, and the Hebrew language was also used by non-Jewish groups, such as the ethnically related Samaritans.
Modern Hebrew is one of the two official languages of Israel (the other being Arabic), while Classical Hebrew is used for prayer or study in Jewish communities around the world. The earliest examples of written Hebrew date from the 10th century BCE [2] to the late Second Temple period, after which the language developed into Mishnaic Hebrew.
Ancient Hebrew is also the liturgical tongue of the Samaritans, while modern Hebrew or Arabic is their vernacular, though today only about 700 Samaritans remain. As a foreign language it is studied mostly by Jews and students of Judaism and Israel, archaeologists and linguists specializing in the Middle East and its civilizations, by theologians, and in Christian seminaries.
The core of the Torah (the first five books of the Hebrew Bible), and most of the rest of the Hebrew Bible, is written in Classical Hebrew, and much of its present form is specifically the dialect of Biblical Hebrew that scholars believe flourished around the 6th century BCE, around the time of the Babylonian exile. For this reason, Hebrew has been referred to by Jews as Leshon HaKodesh (לשון הקודש), "The Holy Language", since ancient times.
source: wikipedia.org
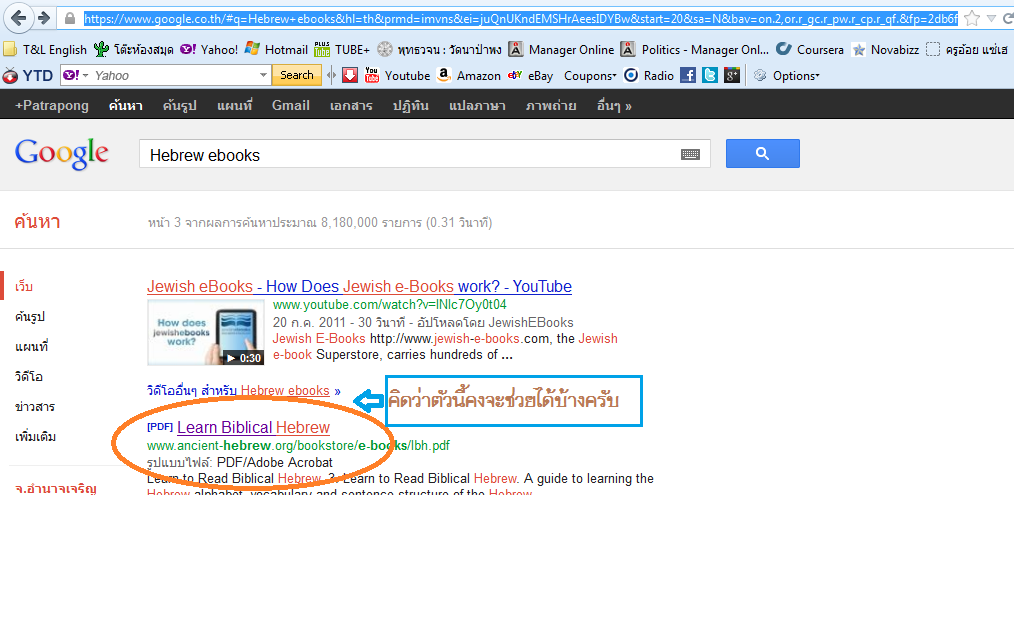
เอาแค่นี้ไปพอไหม เพราะเราก็ไม่ทราบว่าคุณ จขกท อยากเรียนฮีบรูเก่า หรือใหม่ และจะเรียนไปเพื่อจุดประสงค์ใด
| จากคุณ |
:
ปากจัดชะมัดยาด (ปรารถนาดี ไม่มีแอบแฝง) 
|
| เขียนเมื่อ |
:
วันแม่แห่งชาติ 55 22:58:09
|
|
|
|
 |