 |
 ความคิดเห็นที่ 10
ความคิดเห็นที่ 10 |

ขอขอบคุณ:
น้อง THE_AR, ท่าน sparrow, พี่ GreenEyes และกวิวัฏ ที่ช่วยเรื่องเอกสารครับ
เอกสารอ้างอิง
Ben-Ari, E. T. 2000. Birds of a (toxic) feather. Bioscience 50(12), 1136.
Daly, J. 1995. The chemistry of poisons in amphibian skin. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 92(1): 913.
Diamond, J.M. 1992. Rubbish birds are poisonous. Nature 360, 19-20.
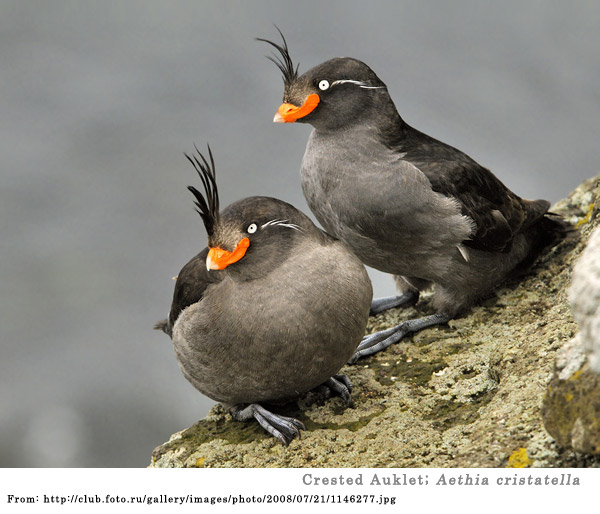
Douglas III, H.D., Co, J.E., Jones, T.H., & W.E. Conner. 2001. Heteropteran chemical repellants identified in the citrus odor of a seabird (crested auklet: Aethia cristatella): Evolutionary convergence in chemical ecology. Naturwissenschaften 88, 330-332.
Dumbacher, J.P. 1999. Evolution of toxicity in pitohuis: I. Effects of homobatrachotoxin on chewing lice (order Phithiraptera). The Auk 116(4), 957-963.
Dumbacher, J. P., Beehler, B. M., Spande, T. F., Garrafo, H. M. & Daly, J. W. 1992. Homobatrachotoxin in the genus Pitohuichemical defence in birds. Science 258, 799801.
Dumbacher, J. P., Beehler, B. M., Spande, T. F., Garrafo, H. M. & Daly, J. W. 1993. Pitohui: How toxic and to whom? Science 259, 582-583.
Dumbacher, J. P., Deiner, K., Thompson, L., Fleischer, R. C. 2008. Phylogeny of the avian genus Pitohui and the evolution of toxicity in birds. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 49(3), 774-781.
Dumbacher, J. P. & Pruett-Jones, S. 1996. Avian chemical defense. Current Ornithology 13, 137-174.
Dumbacher, J.P. & R.C. Fleischer. 2001. Phylogenetic evidence for colour pattern convergence in toxic pitohuis: Mullerian mimicry in birds? Proc R Soc Lond 268, 1971-1976.
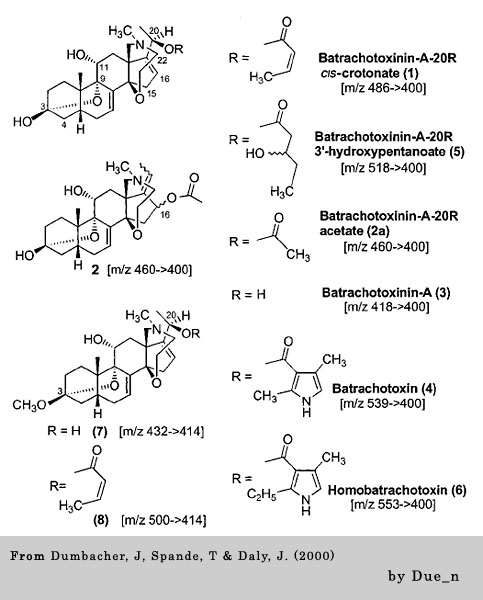
Dumbacher, J. P., Spande, T. F. & Daly, J. W. 2000. Batrachotoxin alkaloids from passerine birds: a second toxic bird genus (Ifrita kowaldi) from New Guinea. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97, 1297012975.
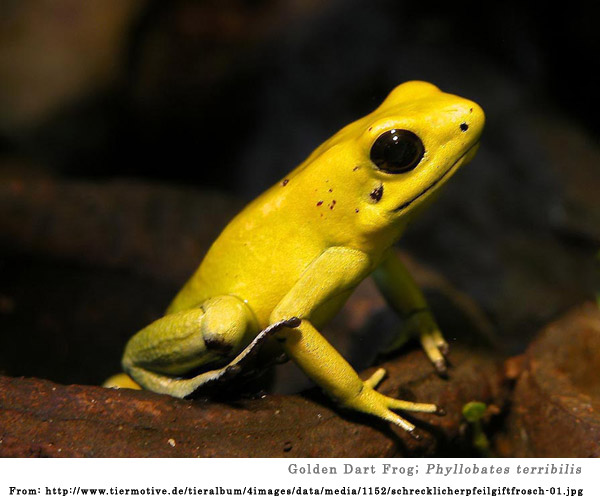
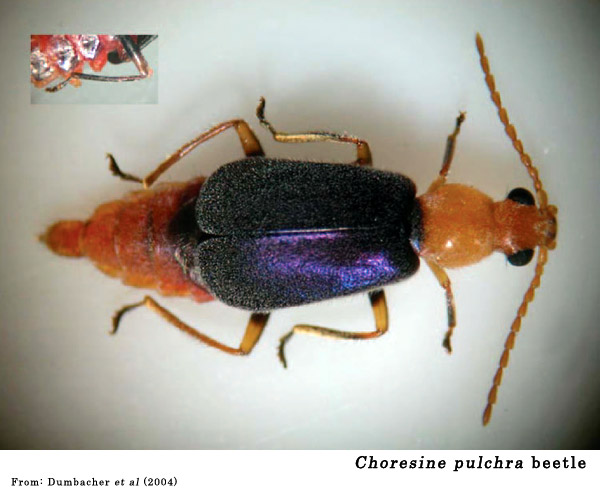
Dumbacher, J. P., Wako, A., Derrickson, S. R., Samuelson, A., Spande, T. F. & Daly, J. W. 2004. Melyrid beetles (Choresine): a putative source for the batrachotoxin alkaloids found in poison-dart frogs and toxic passerine birds. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 101, 1585715860.
Hagelin, J.C. 2007. The citrus-like scent of crested auklets: reviewing the evidence for an avian olfactory ornament. Journal of Ornithology 148, 195-201.
Hagelin, J.C. & Jones, I.L. 2007. Bird odors and other chemical substances: A defense mechanism or overlooked mode of intraspecific communication. The Auk 124(3):121.
Jonsson, K. A., Bowie, R. C. K., Norman, J. A., Christidis, L. and Fjeldsa, J. 2008. Polyphyletic origin of toxic Pitohui birds suggests widespread occurrence of toxicity in corvoid birds. Biol. Lett. 4(1), 71-74.
Legge, S. and Heinshn, R. 1996. Cooperative breeding in Hooded Pitohuis Pitohui dichrous. Emu 96, 139-140.
Mouritsen, K.N. and Madsen, J. 1994. Toxic birds: defense against parasites? Oikos 69, 357-358.
Poulsen, B. O. 1993. Poison in Pitohui birdsagainst predators or ectoparasites. Emu 93, 128129.
Sever, A. 2004. Avian toxicity: Batrachotoxins as chemical defense. Student Review Articles in Chemical Ecology (BI 570). Colorado State University.
Summer, K. and Clough, M. E. 2001. The evolution of coloration and toxicity in the poison frog family (Dendrobatidae). Pro Natl Acad Sci U S A. 98(11), 6227-6232.
Weldon, P.J. 2000. Avian chemical defense: Toxic birds not of a feather. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97, 12948-12949.
| จากคุณ |
:
Due_n   
|
| เขียนเมื่อ |
:
27 ก.ค. 52 00:08:59
|
|
|
|
 |
















 เอากระทู้นี้มาให้คุณดิวจ้า ;)
เอากระทู้นี้มาให้คุณดิวจ้า ;)
 ... เข้ามาดู
... เข้ามาดู



