|
 ความคิดเห็นที่ 50
ความคิดเห็นที่ 50 |

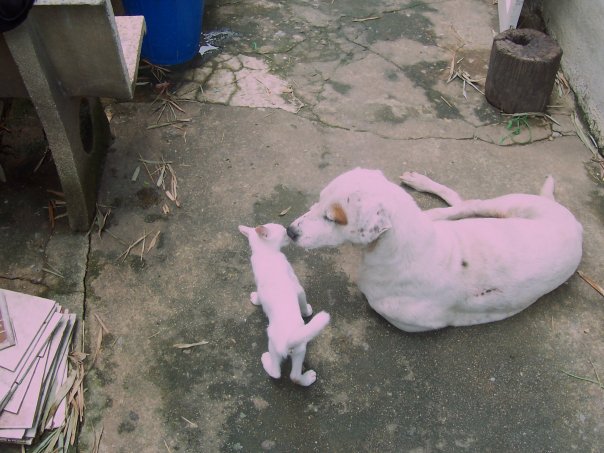
ขอเพิ่มเติมนะครับ พออ่านเรื่องของ จขกท มันทำให้นึกถึงสารคดีที่เคยดูเป็นเรื่องเกี่ยวกับภาวะพึ่งพาอาศัยแบบเดียวกันนี้เรื่องนึง แต่อันนี้ไม่ใช่ระหว่าง สัตว์กับสัตว์ แต่เป็นการพึ่งพิงกันระหว่าง สัตว์กับพืช ซึ่งต่างฝ่ายต่างก็ได้รับผลประโยชน์ด้วยกันทั้งสองฝ่ายวิน วิน
โดยนักแสดงนำของเราก็คือ ต้น Acacia และ น้องมด
ต้องเกริ่นนำถึงต้น Acacia ก่อน มันเป็นต้นไม้ยืนต้นขนาดกลาง-ใหญ่ ถิ่นที่อยู่ก็ได้แก่ ออสเตรเลีย หมู่เกาะแปซิฟิก อเมริกากลาง และ อาฟริกา ต้น Acacia ยังมีชื่อเรียกอื่น ๆ ตามถิ่นที่อยู่และลักษณะพันธุ์ที่แตกต่างกัน เช่น Throntree (มีหนามแหลม), Whistling thron (มีหนามกลวง เวลาลมพัดจะมีเสียงคล้ายเสียงผิวปาก), Yellow fever acacia (มีดอกเหลืองอ๋อย) เติบโตในบริเวณป่าโปร่ง หรือ ทุ่งหญ้าแห้งแล้งแบบสวันนา ออกดอกสีเหลือง ขาว ชมพู บางพันธ์มีหนามแหลม (เพื่อป้องกันแมลงศัตรู หรือสัตว์กินพืชอื่น ๆ) ต้น acacia หลายพันธุ์มีความสัมพันธ์ระหว่างมัน กับมดในรูปแบบที่เข้าใจง่าย ๆ คือ ต้น Acacia จะผลิตของเหลวออกมา เรียกว่า Beltian bodies (ของเหลวที่อุดมไปด้วยโปรตีน มักมีสีแดง หรือเหลือง) ออกมาตรงปลายใบ และยังผลิตน้ำหวาน ที่อุดมไปด้วยคาร์โบไฮเดรต ออกมาตรงก้านใบอีก เรียกว่ามดได้สารอาหารจำเป็นพื้นฐานครบถ้วนจากต้น Acacia และยังใช้ต้น Acacia เป็นบ้านได้อีกด้วย แต่งานนี้ไม่มีกินบนเรือนขี้รดบนหลังคาแน่นอน เพราะมดก็ตอบแทนต้น Acacia ด้วยการเป็น Guard ป้องกันและช่วยกำจัดศัตรูที่จะมากัดกินหรือทำความเสียหายให้กับต้น Acacia อย่างพวกแมลง และ บรรดาอีหน้าหนอนทั้งหลาย
*ขอขอบคุณอากู๋ และ ป้าวิ ในการหาข้อมูลและรูปภาพ **ภาพของต้น Acacia ที่นำมาลงเป็นพันธ์ที่ขึ้นในอาฟริกา ไม่สามารถนำรูปมาลงทั้ง 1,300 สปีชี่ส์ได้
Acacias are also known as thorntrees, whistling thorns or wattles, including the yellow-fever acacia and umbrella acacias.
Bullhorn Acacia is best known for its symbiotic relationship with a species of Pseudomyrmex ant (Pseudomyrmex ferruginea) that lives in its hollowed-out thorns. Unlike other acacias, Bullhorn acacias are deficient in the bitter alkaloids usually located in the leaves that defend against ravaging insects and animals. Bullhorn acacia ants fulfill that role.
The ants act as a defense mechanism for the tree, protecting it against harmful insects, animals or humans that may come into contact with it. The ants live in the hollowed-out thorns for which the tree is named. In return, the tree supplies the ants with protein-lipid nodules called Beltian bodies from its leaflet tips and carbohydrate-rich nectar from glands on its leaf stalk. These Beltian bodies have no known function other than to provide food for the symbiotic ants. The aggressive ants release an alarm pheromone and rush out of their thorn "barracks" in great numbers.
**A Beltian body is a structure found on the leaves of some species of Acacia. Beltian bodies, named after Thomas Belt, are found on the tips of each leaflet and are rich in lipids and proteins and often red in colour. They are believed to have evolved in a symbiotic relationship with ants. The ants live inside special plant structures (Domatia) or near the plant and keep away herbivores. Other ant-mutualism related plant structures include Beccarian, Mullerian and pearl bodies.
แก้ไขเมื่อ 05 ส.ค. 52 19:05:14
แก้ไขเมื่อ 05 ส.ค. 52 19:00:30
| จากคุณ |
:
. (Heg765) 
|
| เขียนเมื่อ |
:
5 ส.ค. 52 18:59:33
|
|
|
|
 |
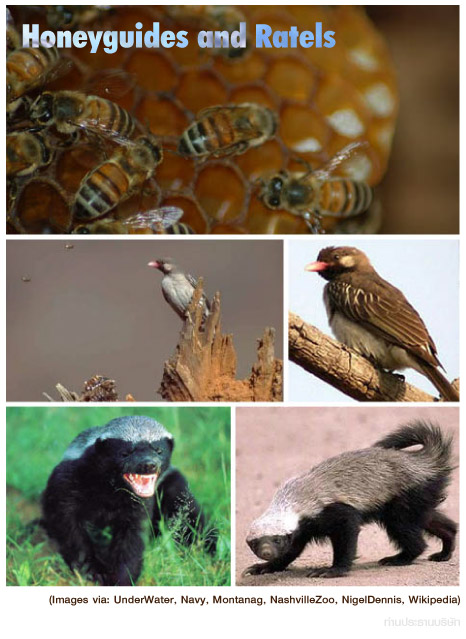
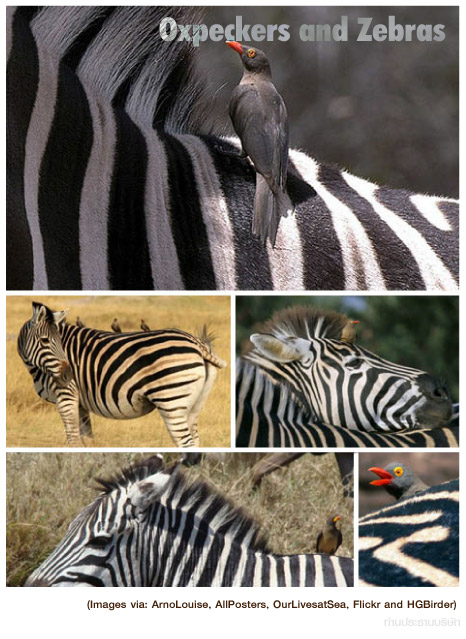
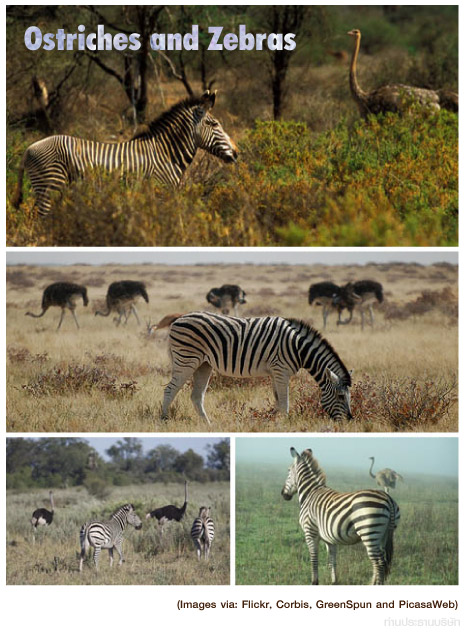
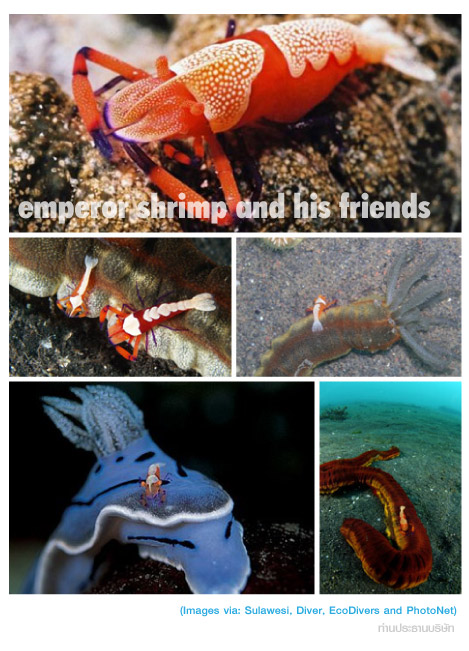
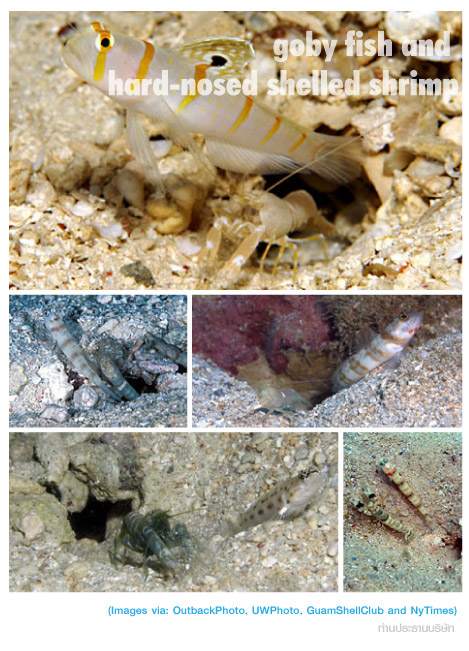
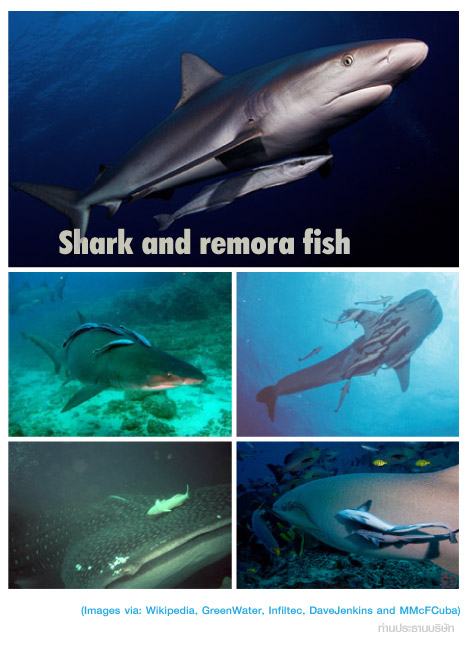
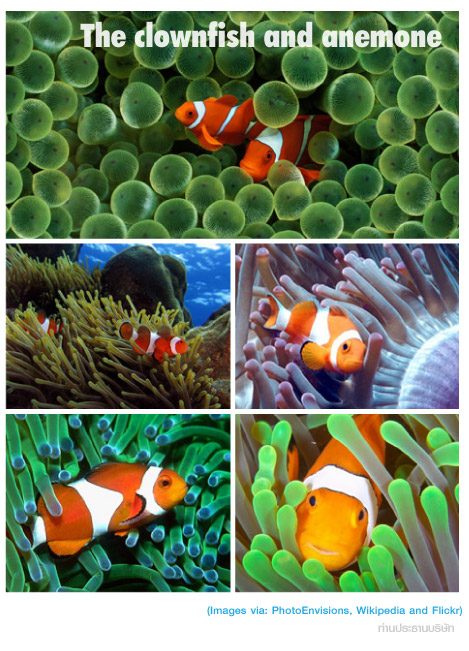






















 ... เข้ามาดู
... เข้ามาดู